-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
So, a few days have gone by. Did I do anything in those days? Well.. Yes. I spent several nights up until ~2 PM or so working on my economic system, mainly on the a diagram for it.
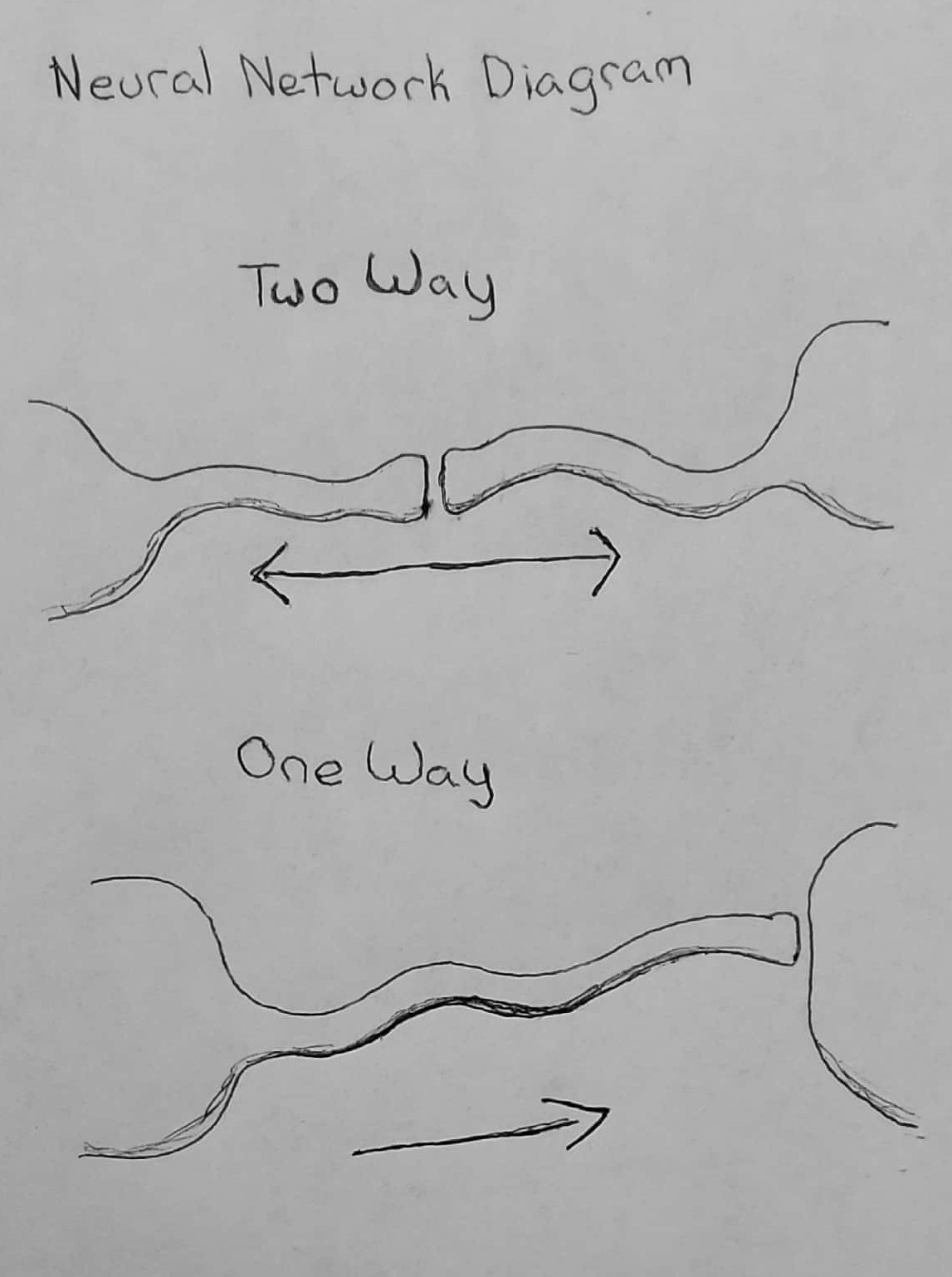
Speaking of which, I created my own type of diagram for this purpose. I call it a Neural Network Diagram (not to be confused with diagrams of neural networks). Here is a quickly drawn demonstration of how it works (I didn't have an eraser):
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
Back to what I was saying...
With that out of the way, let's get acquainted with the reasons behind why I did this in the first place. Why create a new economic system from scratch? Why spend countless hours on something so abstract? What even got into me?
Well, it something I heard from a philosopher that inspired me. I was watching a some video on philosophy, and the person speaking said something along these lines:
"It is possible that the next economic system we have will be both more capitalist than Capitalism and more socialist than Socialism."
These seemed paradoxical, but intriguing, and it sparked my interest into what that would look like. Since there were no current economic models that were both more capitalist than Capitalism and more socialist than Socialism, I decided that patience is a virtue, but also overrated when you have the skill and understanding necessary to make something yourself rather than waiting for someone else to come up with it.
Of course, I had more than just curiosity that inspired me. Capitalism has problems, and more than many people are aware of. Not just the "upper class vs poor people" problems or social injustice that socialists seem to focus so much upon (not that I blame them because it is easy for many people to get caught up in the Tribalism of it all). I am talking about substantial functional and structural flaws that make it flawed at best, and apocalyptic at worst. My view is somewhere in-between, but I digress.
I know many may be unaware of just what makes capitalism insufficient, so I will do you a favor and lay out the inherent internal contradictions and logical flaws within Capitalism, the dominant economic model, and how they are fixed with Intramutualism:
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
 1. The contradiction between capital and labor: In capitalism, owners can increase their profits by paying workers less, while workers seek to maximize their wages and benefits. This creates a fundamental conflict between the interests of owners and the interests of workers.
1. The contradiction between capital and labor: In capitalism, owners can increase their profits by paying workers less, while workers seek to maximize their wages and benefits. This creates a fundamental conflict between the interests of owners and the interests of workers.
From my perspective, it's like having to haggle for prices at a store every time you buy a product, with the clerk trying to charge you more and you trying to pay less, all while the clerk has the power to refuse your purchase if you can't agree on the price. And all of this is made worse because you don't actually know how much the product costed for the store.
This would be inefficient and frustrating, so stores have set prices close to what they paid for the product instead, because it is the only logical option at that scale. Yet with the labor market and jobs, the things we rely on to help keep us fed so we don't starve, that is exactly how it operates. You don't know how much you make for a company (you could gather details and do the math to work it out, but you would be able to do that in the clerk scenario, and it still likely wouldn't get you a raise if you showed this knowledge to your boss. He would probably just look at you funny and suggest some more productive things you could do with your time).
You have to bargain for wages, asking your boss for a raise if you want one. If you and your boss disagree on your wage, either of you can terminate your employment. This is not ideal because it is inherently unstable, and in both situations I highlighted, there is a high likelihood that it will result in a poor person being ripped off by someone with far more resources than them.
It doesn't help that this is exacerbated by the free-rider problem, in this case if a business pays decent wages, they can be undercut by a business paying lower wages, so all businesses must pay decent wages together to maintain them, because if one of them undercuts the others with cheaper labor, the deck of cards collapses.
In that regard, Intramutualism aims to do the logical thing with labor: to keep worker pay on line with the value they produce, rather than funneling most of it upwards to people who did not create that value. In Intramutualism, the pay is consistent with the contribution, and the Rewards Framework makes sure of that. It is more stable, more sensible, more practical, more logical, and, as a whole, more productive and efficient. It would also give workers direct feedback, psychologically framing it less like work and more like a game that can be mastered to achieve the greatest outcome.
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
 2. The contradiction between production and consumption: In order for capitalism to function, goods and services must be produced and sold on the market. However, the workers who produce these goods and services are also consumers. If wages are kept low in order to maximize profits, which is the logical strategy in capitalism, workers will not have enough purchasing power to buy the goods and services they produce. This leads to overproduction and economic crises, or even a case of the not good, very bad, entire economic collapse.
2. The contradiction between production and consumption: In order for capitalism to function, goods and services must be produced and sold on the market. However, the workers who produce these goods and services are also consumers. If wages are kept low in order to maximize profits, which is the logical strategy in capitalism, workers will not have enough purchasing power to buy the goods and services they produce. This leads to overproduction and economic crises, or even a case of the not good, very bad, entire economic collapse.
How is that fixed? Intramutualism doesn't give business owners the power to lower wages. Workers get more wages. Problem solved. Crisis averted. Lives saved.
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
 3. The contradiction between competition and cooperation: Capitalism is based on competition between firms in the marketplace. However, firms also need to cooperate in order to achieve common goals, such as the development of new technologies or the provision of public goods. This can create tension between the individualistic ethos of competition and the need for cooperation in order to achieve social goals.
3. The contradiction between competition and cooperation: Capitalism is based on competition between firms in the marketplace. However, firms also need to cooperate in order to achieve common goals, such as the development of new technologies or the provision of public goods. This can create tension between the individualistic ethos of competition and the need for cooperation in order to achieve social goals.
Meanwhile, Intramutualism only rewards companies for value they put into the economy. If competition between them is detrimental to the economy, it hurts them enough to send the message: Fights of Futility Frequently Fail. This also means that if, by partnering, they can put more value into the economy, then that is the optimal strategy and any competent firm will take that route.
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
 4. The contradiction between short-term and long-term interests: Businesses in Capitalism are driven by the need to maximize profits in the short term. This leads to decisions that are detrimental to the long-term interests of society, such as environmental degradation or the depletion of natural resources. Presto! Instant dystopia! (Pollution flavored, includes natural and toxic flavors. May contain tetraethyl lead.)
4. The contradiction between short-term and long-term interests: Businesses in Capitalism are driven by the need to maximize profits in the short term. This leads to decisions that are detrimental to the long-term interests of society, such as environmental degradation or the depletion of natural resources. Presto! Instant dystopia! (Pollution flavored, includes natural and toxic flavors. May contain tetraethyl lead.)
However, within Intramutualism, doing destructive things means big losses, because destruction creates no value, but it does destroy value, which would lead to punishment for a company. This goes for both long and short-term destruction.
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
 5. The contradiction between consumer and business interests: Under capitalism, firms want to make as much profit as possible by selling goods and services at high profit margins, while consumers want to pay low prices. This can lead to bad practices, such as firms reducing product quality to increase profits or using unethical advertising practices to persuade consumers to buy their products, which can harm consumers and damage trust in the market system.
5. The contradiction between consumer and business interests: Under capitalism, firms want to make as much profit as possible by selling goods and services at high profit margins, while consumers want to pay low prices. This can lead to bad practices, such as firms reducing product quality to increase profits or using unethical advertising practices to persuade consumers to buy their products, which can harm consumers and damage trust in the market system.
In Intramutualism, this is unlikely to happen for several reasons: first, if undercutting competitors with lower-quality products is bad for society or the economy, it will be disincentivized (in the case of overbuilt products, it isn't always bad, so it could still happen, but only if is worth the trade-off). Also, profit for everyone in the company is decided not by how much they sell, and their profit margins, but instead how much value they create.
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
 6. The contradiction between permanent solutions and profit: In Capitalism, businesses seek to maximize profits and generate returns for their shareholders. One way to do this is to maintain demand for their products or services. This can lead to a situation where businesses may avoid permanent and simple solutions that would reduce demand for their products or services, even if such solutions would benefit society as a whole. In capitalism, businesses prioritize profits and generating returns for shareholders, relying on demand for their products or services. This can result in companies avoiding permanent solutions that would reduce demand for their profitable business, even if it would benefit society. For example, companies prioritizing drugs that temporarily treat chronic conditions instead of making actual cures, because they would rather maintain ongoing treatment and profits.
6. The contradiction between permanent solutions and profit: In Capitalism, businesses seek to maximize profits and generate returns for their shareholders. One way to do this is to maintain demand for their products or services. This can lead to a situation where businesses may avoid permanent and simple solutions that would reduce demand for their products or services, even if such solutions would benefit society as a whole. In capitalism, businesses prioritize profits and generating returns for shareholders, relying on demand for their products or services. This can result in companies avoiding permanent solutions that would reduce demand for their profitable business, even if it would benefit society. For example, companies prioritizing drugs that temporarily treat chronic conditions instead of making actual cures, because they would rather maintain ongoing treatment and profits.
Under Intramutualism, there are a few reasons this strategy would not work. First, businesses would have much more incentive to create permanent solutions, as the value created by permanent solutions is going to be higher than lifelong treatment using temporary measures. Also, temporary solutions tend to be more capital-intensive over time, meaning they cost more. Additionally, there are no shareholders in Intramutualism, and profits are tied to the value produced.
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
 7. The contradiction between productivity and external responsibility: In capitalism, companies aim to maximize their productivity and efficiency by minimizing costs. However, this can incentivize externalizing costs onto society and the environment, such as by taking advantage of cheap labor or resources, exploiting public goods and services, placing more of their work on customers, and utilizing political influence to secure special treatment or avoid regulation. These practices can lead to the exploitation of others and harm the social and ecological systems that support them, while benefiting those who engage in them. This is a form of seeking advantage by using external resources, without providing any corresponding value in return.
7. The contradiction between productivity and external responsibility: In capitalism, companies aim to maximize their productivity and efficiency by minimizing costs. However, this can incentivize externalizing costs onto society and the environment, such as by taking advantage of cheap labor or resources, exploiting public goods and services, placing more of their work on customers, and utilizing political influence to secure special treatment or avoid regulation. These practices can lead to the exploitation of others and harm the social and ecological systems that support them, while benefiting those who engage in them. This is a form of seeking advantage by using external resources, without providing any corresponding value in return.
As Intramutualism does not incentivize irresponsibility, this problem is also solved. The companies are only paid by how much net value they produce in Intramutualism, not how saavy they are at passing on their costs to other entities. They would be directly assessed, with all factors taken into account.
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
 8. The contradiction between private enterprise and the public market: Under capitalism, businesses are incentivized to maximize profits by selling products or services that are desirable to customers. However, businesses have more information about their products or services than their customers, which makes customers vulnerable to deceptive marketing and unethical practices. This can result in customers purchasing products or services that do not meet their expectations or needs, which can lead to harm, dissatisfaction, and waste. Such practices can also create a power imbalance, where businesses have an unfair advantage over their customers.
8. The contradiction between private enterprise and the public market: Under capitalism, businesses are incentivized to maximize profits by selling products or services that are desirable to customers. However, businesses have more information about their products or services than their customers, which makes customers vulnerable to deceptive marketing and unethical practices. This can result in customers purchasing products or services that do not meet their expectations or needs, which can lead to harm, dissatisfaction, and waste. Such practices can also create a power imbalance, where businesses have an unfair advantage over their customers.
In Intramutualism, however, businesses have to operate transparently with the Commerce Connection System. Since they all must release this knowledge, and it is in public access, there are no secrets to keep. Also, shady business tactics would be heavily disincentivized.
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
 9. The contradiction between competition and concentration: Capitalism creates a competitive environment where firms strive to gain market share and dominate their industry. However, this frequently leads to a concentration of market power, with a few dominant firms controlling a significant portion of the market, limiting competition and creating barriers to entry for new competitors. This results in higher prices for consumers, lower wages for workers, and less innovation as dominant firms prioritize maintaining their market position over taking risks and innovating.
9. The contradiction between competition and concentration: Capitalism creates a competitive environment where firms strive to gain market share and dominate their industry. However, this frequently leads to a concentration of market power, with a few dominant firms controlling a significant portion of the market, limiting competition and creating barriers to entry for new competitors. This results in higher prices for consumers, lower wages for workers, and less innovation as dominant firms prioritize maintaining their market position over taking risks and innovating.
In Intramutualism, first off, as these are also shady business tactics, they would be heavily disincentivized. Additionally, the support for Startups significantly lowers barriers to entry, and while technically probably not immune to monopolies in some areas, they would not be able to cause harm anywhere close to the harm monopolies in Capitalism achieve. Also, if there were monopolies, they would likely only form in niche areas, and monopolies would not be helped with incentives for, rather than state-sanctioned monopolies on, specific inventions. In other words, incentives rather than Intellectual Property. That way companies cannot hoard intellectual property and use it to rent-seek their way to the top like they can in Capitalism.
There. Those were the biggest problems with Capitalism I could find, and my system fixes all of them. Theoretically, at the very least.
Also, I wrote a poem while I was researching Capitalism for this purpose, so enjoy:
-~-~ Capitalism ~-~- 
-~-~ Capitalism ~-~-
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
You may think it's effective,
I think it's a joke,
It is clearly defective,
For decades it's been broke
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
I can't watch while my future
Disappears up in smoke
Our world's caught in the fire
It continues to stoke
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
So I will propose
A solution for those
Those that wish to dispose
Of what it can impose
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
On the working, the poor
Desperate, hurting, and sore
Those whose life is a chore
With no future in store
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
If we are still believing
In spite of those deceiving
In our skill for achieving
The future we are weaving
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
Then achieve it we will
Let us strive to instill
Through our goodness and will
What we wish to fulfill
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
Let's create a new system
With knowledge, fact, and wisdom
Our world may be ablaze
But it's only a phase
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
If we rise above lies
To reveal its disguise
All of which we dispise
Will then bring its demise
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
The parts made in bad taste
And its problems erased
Once it has been disgraced
And is scrapped and replaced
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
So let's go, let's succeed
Seven billion freed
From this archaic creed
That neglects what we need
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
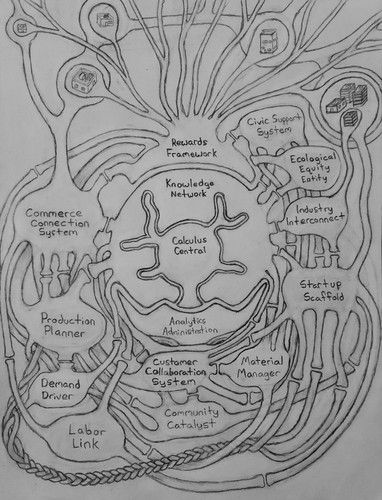
And, with that out of the way, remember the diagram I talked about? Well, here it is, along with a (revised) description of the function of each entity within it shown below:
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
-~-~-~-Intramutualism-~-~-~-
--- Descriptions For Each Entity ---
 Analytics Administration:
Analytics Administration:
Gathers important economic data that other systems cannot or do not provide, and fills in information gaps within the system.
Description 
Gathers necessary economic information for the smooth functioning of the system. Performs social impact assessments, meta-analyses, opinion surveys, behavior analyses, system analyses, aggregation of big data, and creation of economic models, simulations, algorithms, and machine learning systems. Works extensively on data collection, data interpretation, and data representation. Feeds this information into the Knowledge Network, where it is available to all.
 Knowledge Network:
Knowledge Network:
Stores, coordinates and relays information among all systems using integrated communication systems.
Description 
Stores all information fed into it. Coordinates and relays information among all systems, allocating relevant data to systems reliably and efficiently using two systems of communications, the data transfer system and the knowledge transfer system.
The data transfer system is based on communications infrastructure and technology. This consists of a vast electronic communication network, information routing systems, and data storage vaults. It facilitates the distribution of data among the various systems, ensuring they function as a well-coordinated, interconnected whole that sends the right information to the right places at the right times.
The knowledge transfer system is based on direct human interaction. It consists of a network of meeting rooms and videoconference booths, both of which feature devices for recording conversations, so they can be referenced during training, education, or future academic discussions. This system includes a networking, logistics, and scheduling system to keep everything running smoothly. It functions to facilitate the sharing of expertise and knowledge among academics, professionals, and students, so valuable knowledge can be passed on and built upon from generation to generation.
Optional 
Runs a publicly funded internet service using their digital communications infrastructure, providing a platform for websites, many of which would be socially and economically beneficial, thanks to the incentives that are set in place by the Rewards Framework. Free hosting for websites, within reason, could be a feature as well.
 Calculus Central:
Calculus Central:
Makes economic calculations upon the request of other systems.
Description 
Has full access to all economic data within the Knowledge Network. Employs talented problem-solvers, creative geniuses, and many other strains of intellectual talent. This pool of human ingenuity is supplemented with a vast array of tools: machine learning along with other artificial intelligence methods and algorithms, multitudes of different economic models, economic simulations, and anything else of use for predicting the economy. All of this intellectual power is used to predict future economic conditions, and calculate optimal economic strategies, when such is requested by the other entities in the system.
Optional 
When all external requests are fulfilled, operates autonomously. When autonomously operating, works on solutions to existing economic problems, and also on improvements to the system itself. Improvements that improve the design and function of the economic system.
 Rewards Framework:
Rewards Framework:
Allocates pay according to contribution.
Description 
Delegates calculations to Calculus Central to allocate optimal total pay to each company based on their societal and economic contribution, while accounting for externalities. Then, for each company, distributes the allocated company pay based on economic contribution of workers and owner(s).
Optional 
Every time a company hires a worker from a lower productivity area, the leader of the company receives a boost of income, providing an incentive to nudge more productive sectors into expanding their workforce, and thus overall productivity, while also helping to lower unemployment.
Optional 
Requires companies to have transparent reporting of their bureaucratic structure according to formal guidelines which convey the roles and responsibilities of specific people within the workforce.
Optional 
Uses productivity tracking tools, in order to reliably track productivity, independently of the companies. Using that data, can advise companies on ways to increase productivity.
Optional 
Idea database, where employees are instructed to log their ideas before sharing them among the company, so it can be verified that it was their idea, meaning they can be compensated for any value increase their idea results in within the company. Allows employees to claim ownership of ideas before they tell anyone, so others cannot claim ownership of their ideas.
Optional 
Places economic value of a species based on the overall economic and scientific value of the species, factoring in things like ecological dynamics by increasing estimated value with every species reliant on it, as well as genetic uniqueness, by estimating how much genetic history would be erased were it to go extinct. All this is calculated through Calculus Central, and the end result is the estimated value of the species. To find the value for each individual within a species, the value of a species is divided by its population size, or something similar. If a company kills ecological growth directly or indirectly, the value of the ecological growth destroyed is taken from their funding.
 Startup Scaffold:
Startup Scaffold:
Provides a framework that makes it easy to start small businesses.
Description 
Makes efficient system designs for small businesses to follow, which lowers the barriers to entry by decreasing the effort it takes to organize a company.
Optional 
Also assists groups of small businesses so they can easily deal with regulations, industry complexity, management, and other difficulties.
Optional 
Collaborates with the Customer Collaboration System to inform startups about the wishes of customers, so they can fulfill them.
 Labor Link:
Labor Link:
Guides workers to the most suitable jobs available for them.
Description 
Collects comprehensive worker data, including past careers, training, employment status, interests, and other relevant information to pair workers with compatible jobs, which is then stored in the Knowledge Network, for use by them and other branches.
Optional 
Partners with schools to introduce children to jobs that follow child-friendly guidelines, providing training, motivation, familiarization, and a rite of passage.
Optional 
Collaborates with Startup Scaffold so startups have priority within a large labor pool, improving the chances of success for small businesses.
 Material Manager:
Material Manager:
Helps manage the economy's resources more efficiently to prevent waste.
Description 
Specializes in finding new uses for trash and preventing waste. Works with companies, cities, and customers to obtain valuable waste products before they're thrown away, and optimizes their use for profit. Works with companies to reduce waste through new materials and designs.
Optional 
Helps innovate technologies for repurposing waste.
Optional 
Works with Commerce Connection System to improve standards in regard to reusability, longevity, and wastefulness.
Optional 
Collaborates and negotiates with Civic Support System to improve design of products for both customer usefulness and waste management.
 Commerce Connection System:
Commerce Connection System:
Shares knowledge and promotes standards across industries.
Description 
Collects and shares knowledge to promote cross-compatibility and stronger industry-wide standards. Gathers and shares valuable insights on production techniques, management methods, and social innovation to improve the industry.
Optional 
Collaborates with Rewards Framework to reward companies for creating new practices and penalizes those who don't abide by standards.
 Demand Driver:
Demand Driver:
Promotes sales of good products and impedes sales of bad products.
Description 
Uses marketing techniques and price manipulation to promote societally and economically beneficial products, while reducing demand for societally and economically harmful products. Similar to algorithm boosting and shadow banning, but in the economy.
Optional 
Collaborates with Startup Scaffold to give small companies advice on how to make products that are beneficial to society and thus will get demand boosted.
Optional 
Collaborates with Production Planner to make sure it doesn't boost demand beyond the capacity of supply, and that boosts in demand and boosts in supply can be coordinated effectively.
 Customer Collaboration System:
Customer Collaboration System:
Gets input from customers and gives it to industry so they know what customers want.
Description 
Runs surveys and questionnaires among customers to prioritize aspects of products based on their experience. Gathers feedback on quality versus cost and allows customers to suggest changes. Accepts input from customers at any time through various channels. Uses this knowledge in collaboration with Startup Scaffold and Commerce Connection System to help keep industry goals in line with consumer preferences. Increases the amount of choice customers have for things.
Optional 
Gives Startup Scaffold information first, so the small businesses have a head start.
Optional 
Runs a social media platform tailored to acquire useful customer input and ideas, and sends companies a list of all posted product concepts proposed by people on the platform. The most popular concepts, which have higher potential, would be at the top of the list. Thus, the most desired products would be prioritized.
 Production Planner:
Production Planner:
Ensures that there is ample supply to meet demand.
Description 
Collaborates with Customer Collaboration System and Industry to ensure supply meets demand in quantity, quality, and price. Delegates calculations to Calculus Central to determine current and future demand and gives the results to the Rewards Framework so they can allocate funds to producers accordingly in return for them supplying the goods to fulfill that demand.
 Civic Support System:
Civic Support System:
Works to make life simpler so people have more free time to achieve personal goals.
Description 
Connects domestic life to the economy. Works with Commerce Connection System, Startup Scaffold, and industry to improve the design of homes, appliances, and other things in order to reduce domestic burdens for citizens and subsequently free up their time for recreational or economically valuable activities.
Optional 
Helps coordinate services like childcare (which includes babysitting), cleaning, house and product repair, and more. This serves to free up time for people so it can be used for recreational or economically valuable activities.
 Community Catalyst:
Community Catalyst:
Ensures towns and cities develop in a manner that is beneficial and productive for society.
Description 
Shapes the policies, guidelines, and building codes that the Commerce Connection System requires construction businesses to conform to. Ensures that cities and towns develop efficiently and in ways that benefit their occupants, via the Rewards Framework. Helps prevent regrettable mistakes, and works to form cities with a healthy social fabric, strong civil society, widespread collective consciousness, and good public services.
Optional 
Provides low-cost housing for the economically disadvantaged to help them participate in the economy.
Optional 
Works with Startup Scaffold to facilitate the development of business in newly developed towns.
 Industry Interconnect:
Industry Interconnect:
Serves as a route for startups to play supporting roles in the function of the economic system itself.
Description 
Works with the Startup Scaffold to provide a path for new businesses to work as part of the economic system, where the Rewards Framework compensates them based on the value they provide to the system. Ensures consistent evolution and innovation in line with the industry to maintain a healthy system that runs it. This system should in theory, based on the incentives given, make the entire system evolve in the most optimal way to maximize the economy's potential as a whole.
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
So, what do you think? Are there any flaws in Intramutualism, or the logic it relies on? What are your thoughts, ideas, and opinions on it? Do you think it would work?
I haven't got much feedback on this lately, but after the amount of effort I have put into it, any feedback is valuable for me. Thanks, and wish me luck. Intramutualism is still being developed, but it may be finished soon.
Also, I will probably create a less abstract and more straightforward diagram for those that have a hard time understanding the one I made. Does anyone know of any free software to make diagrams with that is easy to use and creates decent diagrams? The only ones I have found so far have been more difficult to use than a pencil and paper, and the actual end results look worse as well.
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- edited 52×, last 15.06.23 10:28:35 am
 Intellectual property is dropped entirely. Instead, the following system is put in place: The inventor and company/division are acknowledged in the filing of an invention, but not given exclusive rights to it. Instead, to incentivize innovation, there are funding incentives. These would actually produce more concrete incentives, because they mean that inventors could actually make a living off of their inventions without taking excessive risk or requiring excessive up-front investment. Being an inventor would finally be an actual stable job, and companies could compete fairly without patent battles. Also, schooling quality would dramatically increase, as all the proprietary information would now be free for public access.
Intellectual property is dropped entirely. Instead, the following system is put in place: The inventor and company/division are acknowledged in the filing of an invention, but not given exclusive rights to it. Instead, to incentivize innovation, there are funding incentives. These would actually produce more concrete incentives, because they mean that inventors could actually make a living off of their inventions without taking excessive risk or requiring excessive up-front investment. Being an inventor would finally be an actual stable job, and companies could compete fairly without patent battles. Also, schooling quality would dramatically increase, as all the proprietary information would now be free for public access. Standardization and cooperation: Enforced standardization. Do we really need 500 different kind of power tool batteries and chargers when one would suffice?
Standardization and cooperation: Enforced standardization. Do we really need 500 different kind of power tool batteries and chargers when one would suffice? Priority: Instead of things like profit determining the amount that can be spent on research and development for something, the return on investment for the good of society would be what determines the amount of funds to be granted, along with the effect one area has on other sectors. With this would come the need for new, more complicated metrics of value to be created. While this might seem like a nuisance, it is a good thing because it would allow us to question the metrics we use to determine value in general, and because such metrics would serve a lot more essential human needs than metrics like GDP. Because of such metrics being used when determining incentives, quality of life would dramatically increase, bring productivity and innovation up with it.
Priority: Instead of things like profit determining the amount that can be spent on research and development for something, the return on investment for the good of society would be what determines the amount of funds to be granted, along with the effect one area has on other sectors. With this would come the need for new, more complicated metrics of value to be created. While this might seem like a nuisance, it is a good thing because it would allow us to question the metrics we use to determine value in general, and because such metrics would serve a lot more essential human needs than metrics like GDP. Because of such metrics being used when determining incentives, quality of life would dramatically increase, bring productivity and innovation up with it. New Economic System
New Economic System
 1
1 

 Offline
Offline

 First, resource allocation is much more efficient and fair. Because there is not as large of a divide between rich and poor, there would be less people spending money on extravagant things that aren't of much practical value simply because they have too much money to know how to use properly, yet more people with financial means to achieve growth (reducing poverty as well).
First, resource allocation is much more efficient and fair. Because there is not as large of a divide between rich and poor, there would be less people spending money on extravagant things that aren't of much practical value simply because they have too much money to know how to use properly, yet more people with financial means to achieve growth (reducing poverty as well).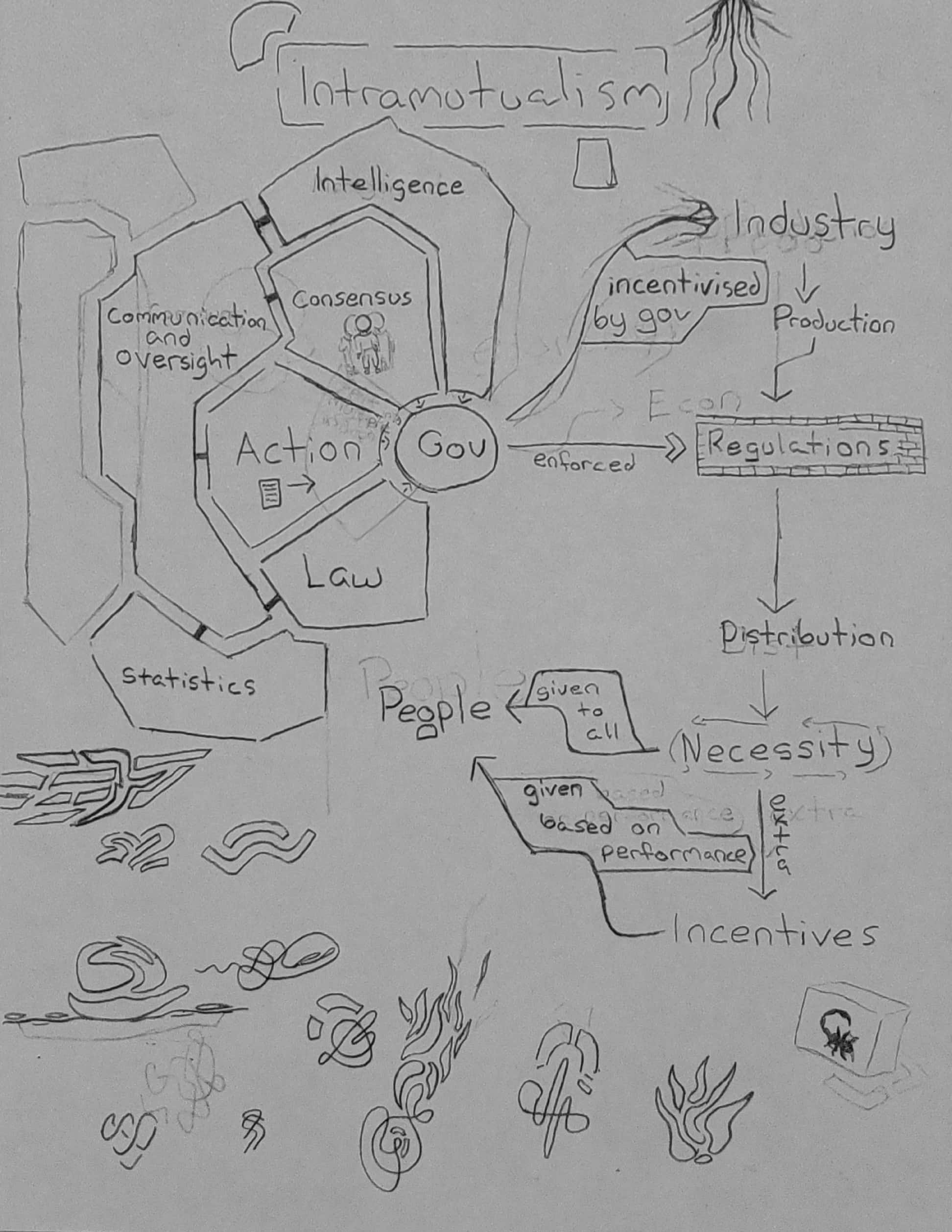
 Gaios
Gaios


